State of Student Aid in Texas – 2022
Section 8: Texas College Attainment
- College Graduates Earn Far More Than High School Graduates and Experience Less Unemployment
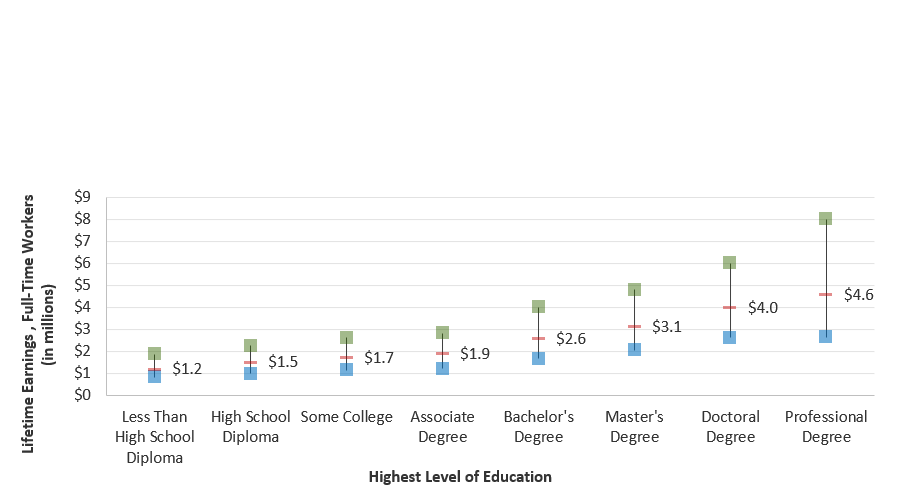
- Better-Educated Workers Have Higher Lifetime Earnings
- One-Third of Texans Age 25 and Older Have a Bachelor’s Degree
- Bachelor’s Degree Attainment Varies by Texas Region
- Graduation Rates in Texas Rising, But Remain Stratified by Race/Ethnicity
- Texas Undergraduates Who Took Developmental Education Courses Were Less Likely to Graduate
- Texas Ranks Low in Percentage of Young Adults with a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher
- Many Texas Students Exit the Education Pipeline Toward a Higher Education Degree or Certificate at Transition Points
- More Than 40 Percent of Low-Income Students Nationwide Dropped Out Within Six Years of Starting College
- Low-Income Texas Students are Far Less Likely to Obtain Bachelor’s Degree Than High-Income Peers
- Four in Five African-American Texas Bachelor’s Degree Graduates Had Borrowed Student Loans
- HBCU Bachelor’s Degree Recipients Borrowed a Median Cumulative Amount of Over $43,000
College Graduates Earn Far More Than High School Graduates and Experience Less Unemployment
Annual Earnings, Full-Time U.S. Workers: 25th, 50th, and 75th Percentiles (2020)
Unemployment Rate by Educational Attainment (2019 through 2022, Seasonally Adjusted)
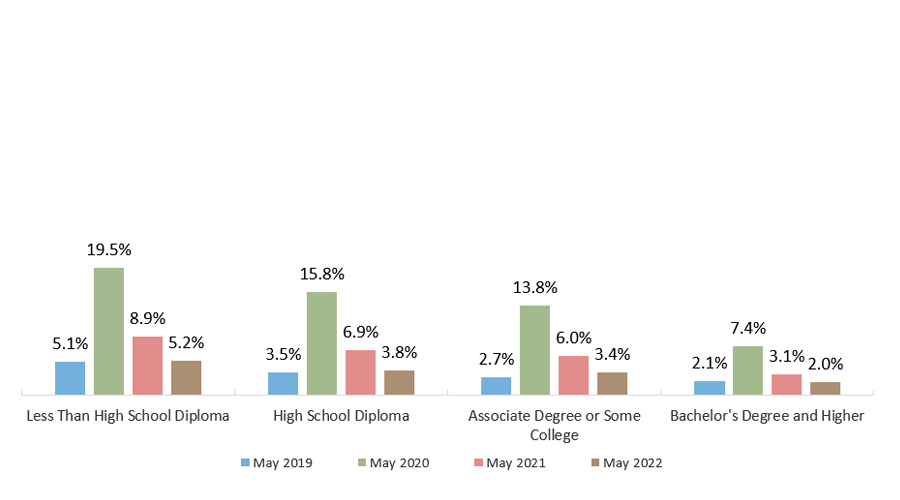
Sources: Unemployment: Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Employment Status of the Civilian Population 25 Years and Over by Educational Attainment,” May 2022 (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.t04.htm); Historical Unemployment Rates: Bureau of Labor Statistics. Data Retrieval: Labor Force Statistics (CPS) (https://www.bls.gov/webapps/legacy/cpsatab4.htm); Earnings: U.S. Census Bureau, American Community Survey 2020 (http://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs/data/pums.html).
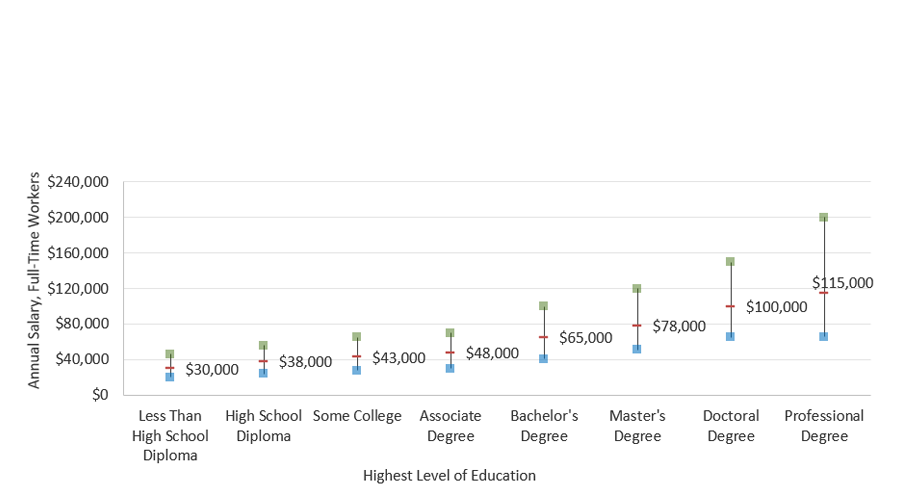
Better-Educated Workers Have Higher Lifetime Earnings
Lifetime Earnings, Full-Time U.S. Workers: 25th, 50th, and 75th Percentiles
(in Millions of 2020 Dollars)
Median Work-life Earnings of Full-Time U.S. Workers by Level of Education and Gender (in millions of 2020 dollars)
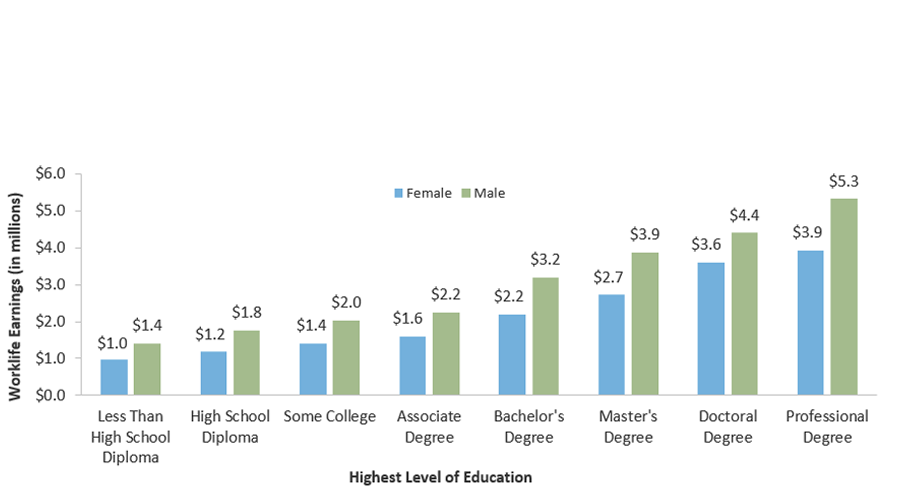
Sources: U.S. Census Bureau, American Community Survey 2020 (http://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs/data/pums.html).
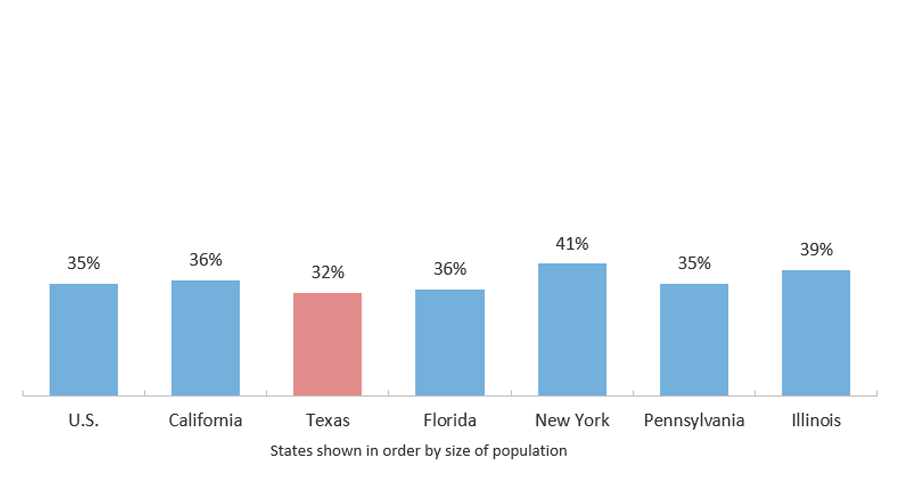
One-Third of Texans Age 25 and Older Have a Bachelor’s Degree
Population Age 25 and Older with a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher (2018)
Population Age 25 and Older with a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher by Race/Ethnicity (2018)
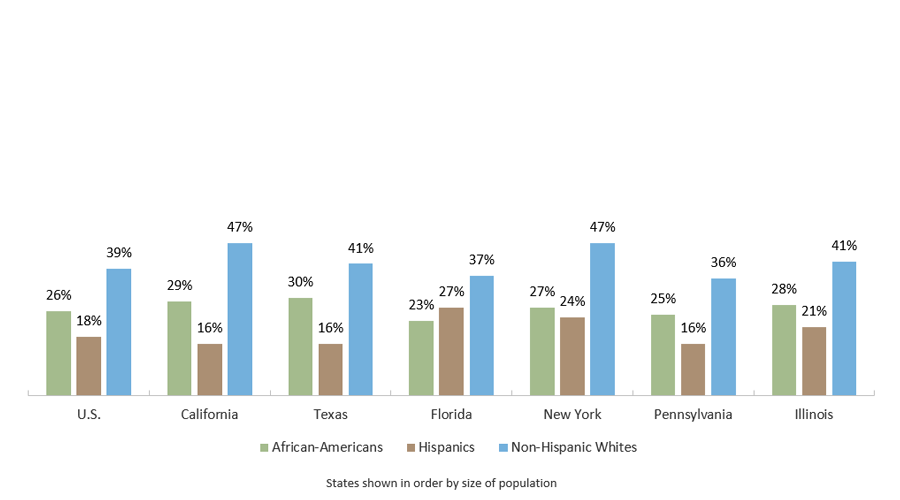
Sources: U.S. Census Bureau, Current Population Survey 2018. Current Population Survey (CPS) Table Creator For the Annual Social and Economic Supplement (https://www.census.gov/cps/data/cpstablecreator.html).
Bachelor’s Degree Attainment Varies by Texas Region
Population Age 25 and Older with a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher (2020)
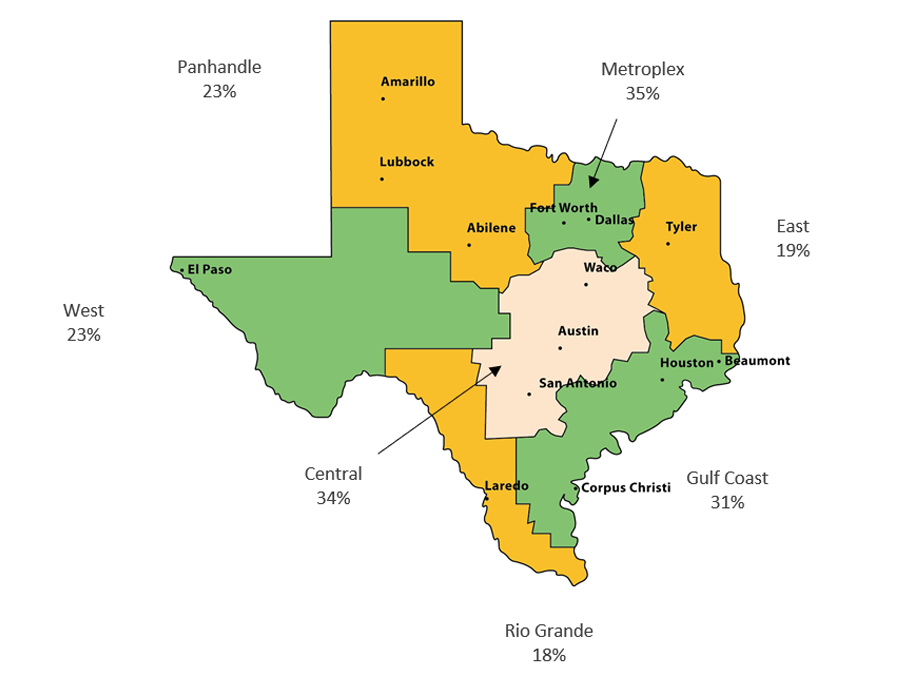
Sources: U.S. Census Bureau, American Communities Survey, 2020 Five-Year Estimates, Washington, D.C. (http://www.census.gov/acs/www/).
Graduation Rates in Texas Rising, But Remain Stratified by Race/Ethnicity
First-time Freshmen Who Entered a Texas Public University and Received a Bachelor’s Degree within Six Years, by Ethnicity
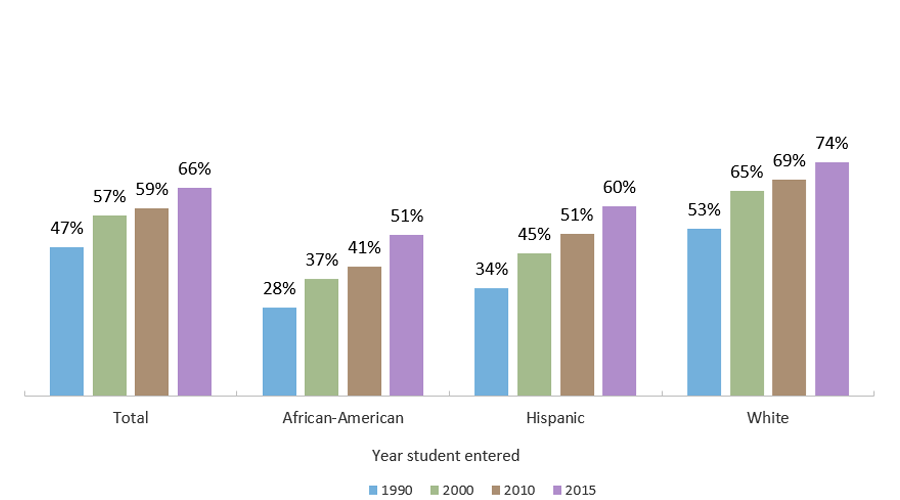
Sources: Graduation rates: Six-year: THECB, Baccalaureate Graduation Rates (http://www.txhigheredaccountability.org/AcctPublic/InteractiveReport/Predefined).
Texas Undergraduates Who Took Developmental Education Courses Were Less Likely to Graduate
Percentage of First-Time, Full-Time Texas Undergraduates Who Graduated or Are Still Enrolled, by Sector and Developmental Education Status
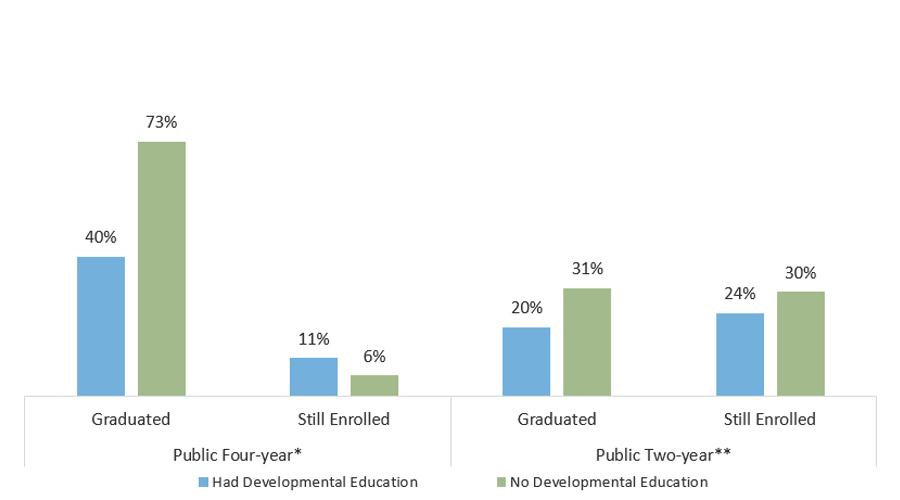
* In 2021 for first-time, full-time students entering in fall 2015. The missing percentage is the percentage of students who had not graduated or were not still enrolled six years after entering postsecondary education.
** In 2021 for first-time, full-time students entering in fall 2018. The missing percentage is the percentage of students who had not graduated or were not still enrolled three years after entering postsecondary education.
Sources: Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board (THECB), Graduation and Persistence of Developmental Education Students (http://www.txhighereddata.org/index.cfm?objectId=200A40A0-E156-11E8-BB650050560100A9); Developmental Education Reforms: U.S. Department of Education, January 2017, “Developmental Education Challenges and Strategies for Reform” (https://www2.ed.gov/about/offices/list/opepd/education-strategies.pdf).
Texas Ranks Low in Percentage of Young Adults with a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher
Percentage of Adults in 2021 (Ages 25-64) With a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher

Note: The methodology and design for this figure was derived from the Texas Business Leadership Council and NCHEMS, 2013 TAB Higher Education Summit.
Sources: OECD (2021), Education at a Glance 2021: OECD Indicators, OECD Publishing, Paris.
DOI: http://www.oecd.org/education/education-at-a-glance/; U.S. Census Bureau, Current Population Survey 2020. Current Population Survey (CPS) Table Creator For the Annual Social and Economic Supplement (http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/cpstc/cps_table_creator.html).
Many Texas Students Exit the Education Pipeline Toward a Higher Education Degree or Certificate at Transition Points
Texas Student Pipeline by Race/Ethnicity, Transition Rates from 8th Grade to College Completion
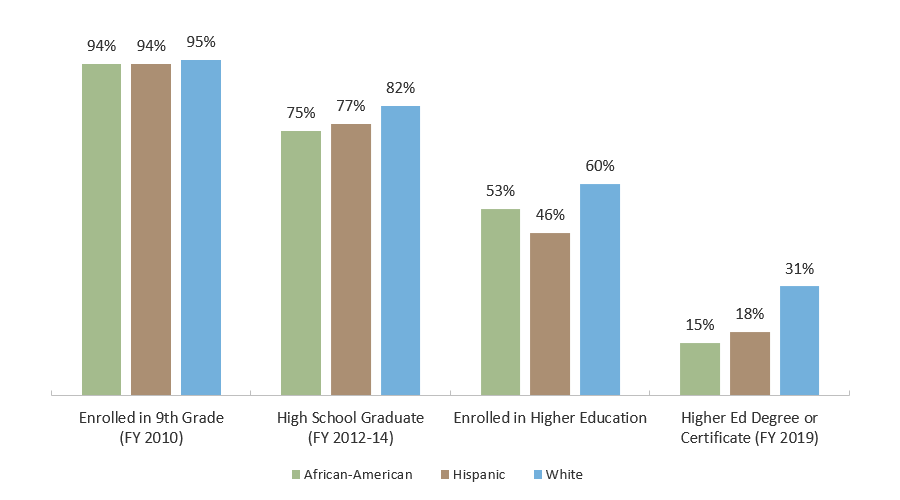
Note: The methodology and design for this figure was derived from the Texas Business Leadership Council and NCHEMS, 2013 TAB Higher Education Summit.
Sources: Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board, Regional Topic Data Tabs: 8th Grade Cohort and HS to College Data, 2019 (http://www.txhighereddata.org/index.cfm?objectId=4E600400-D970-11E8-BB650050560100A9). TEA and National Student Clearinghouse data used by THECB. Out-of-state graduate total not shown, because current NSC data collection extends only into 2006.
More Than 40 Percent of Low-Income Students Nationwide Dropped Out Within Six Years of Starting College
Six-year Attainment Status of 2011-12 First-year Students by Income Quartile
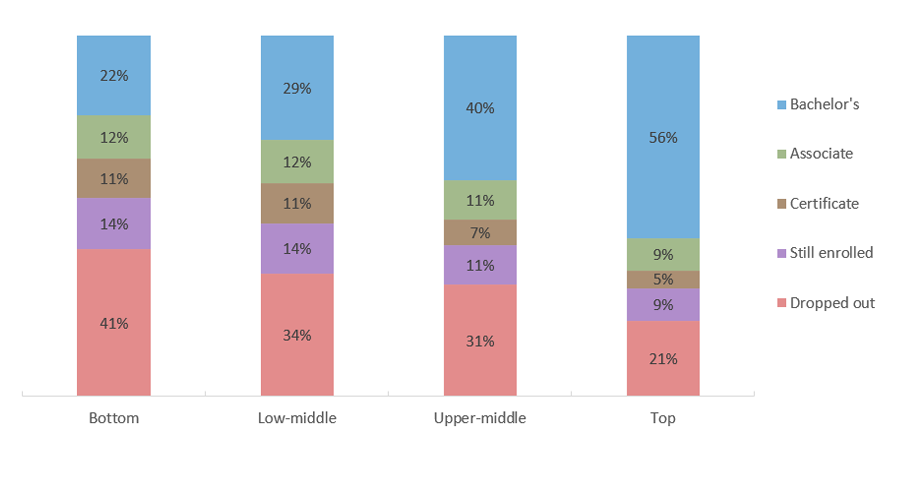
Sources: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, 2012/2017 Beginning Postsecondary Students Longitudinal Survey (BPS: 12/17) (https://nces.ed.gov/surveys/bps/).
Low-Income Texas Students Are Far Less Likely to Obtain Bachelor’s Degree Than High-Income Peers
Baccalaureate Graduation Status by 2015 Income, 2013-14 Texas Public High School Graduates Enrolled in Fall 2014 in Texas Higher Education
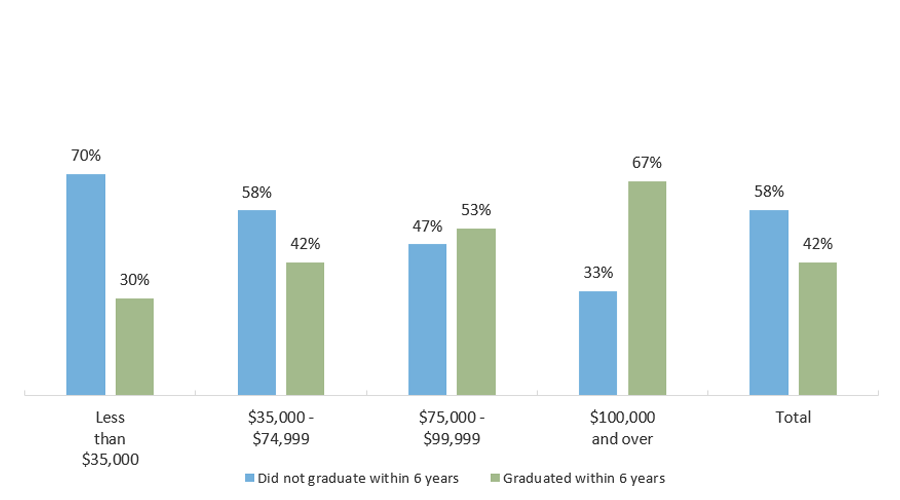
* Expected family contribution is determined through a federal formula that considers family size, income, and the number of children in college, among other factors. It is considered a rough estimate of a reasonable, affordable annual payment for a family with a given set of circumstances.
Sources: Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board (THECB), “Baccalaureate Graduation Status within Six Years by Income Range” (unpublished tables; special request).
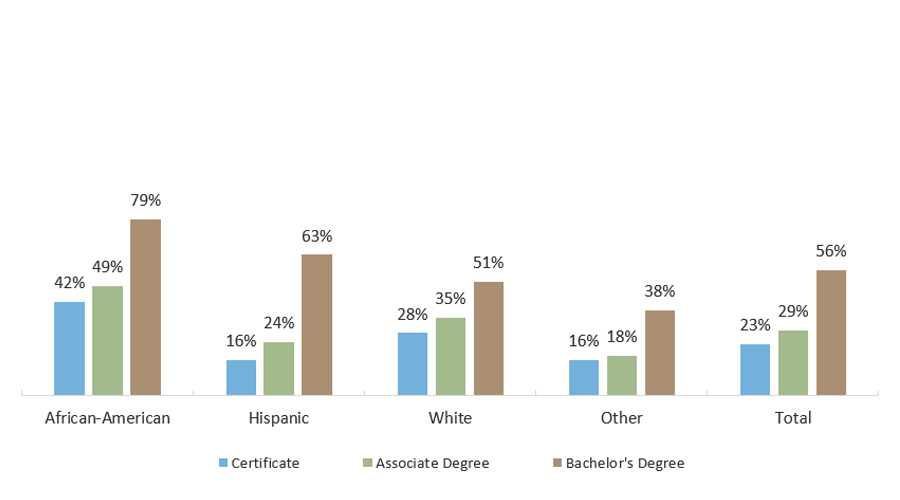
Four in Five African-American Texas Bachelor’s Degree Graduates Had Borrowed Student Loans
Percentage of Texas Graduates with Student Loans, by Degree Level and Race/Ethnicity (FY 2020 Graduates)
Median Loan Amount For Texas Graduates with Student Loans, by Degree Level and Race/Ethnicity (FY 2020 Graduates)
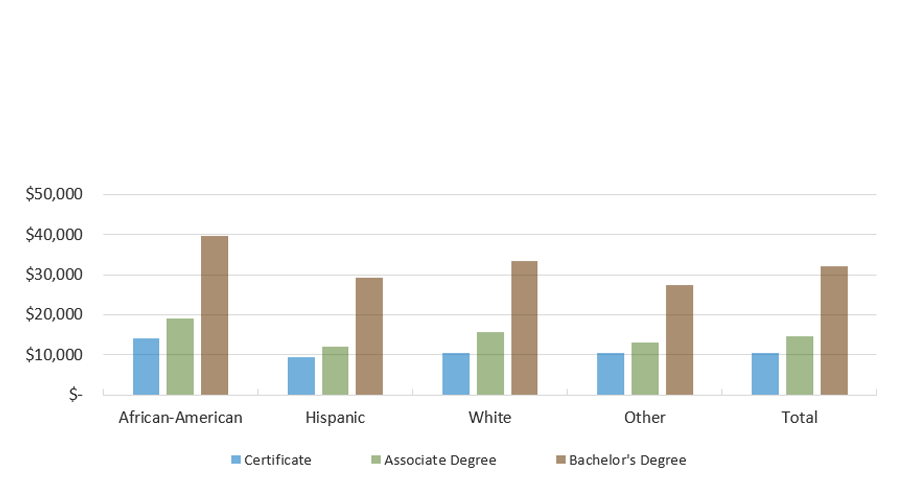
Sources: Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board (THECB), “Median Indebtedness by Degree Level and Race/Ethnicity” (unpublished tables; special request).
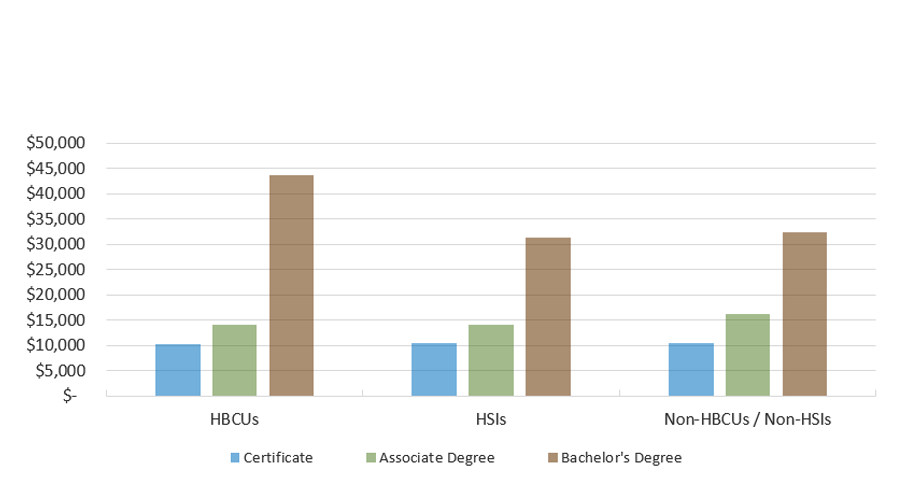
HBCU Bachelor’s Degree Recipients Borrowed a Median Cumulative Amount of Over $43,000
Median Loan Amount for Texas Graduates with Student Loans, by Degree Level and School Group (FY 2020 Graduates)